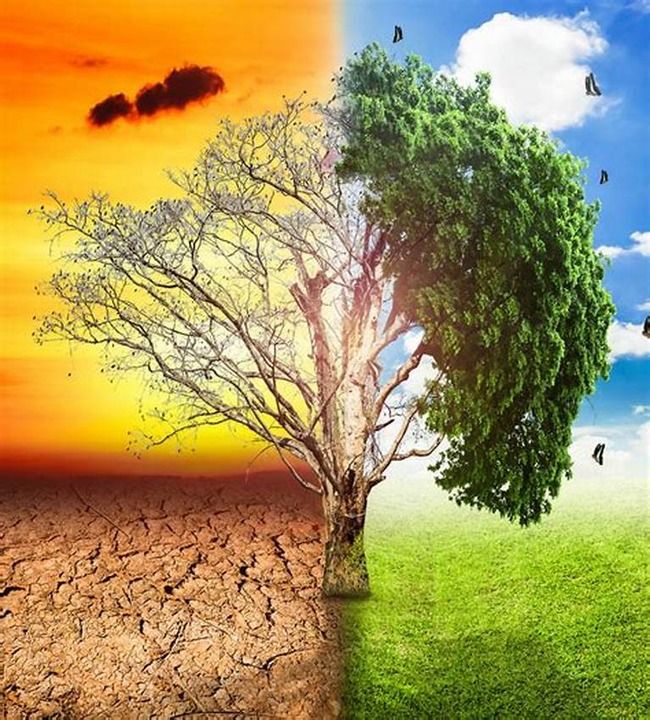
In recent decades, the ominous spectre of climate change has cast its shadow across the globe, leaving no corner untouched. The consequences of this environmental crisis are far-reaching, affecting not only the delicate balance of our ecosystems but also posing significant threats to human health, economies, and social structures. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the multifaceted impact of climate change, examining the interconnected web of challenges it presents and the urgent need for collective action.
Rising Temperatures and Extreme Weather Events:
One of the most apparent and immediate effects of climate change is the rise in global temperatures. Over the past century, the Earth’s average temperature has increased, leading to a surge in extreme weather events. From devastating hurricanes and typhoons to prolonged heatwaves and severe droughts, communities worldwide are grappling with the amplified frequency and intensity of these climatic anomalies. Such events not only endanger lives but also strain infrastructure, disrupt agricultural patterns, and trigger widespread economic losses.
Melting Ice Caps and Rising Sea Levels:
The warming climate has triggered the accelerated melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, contributing to the rise in sea levels. Coastal regions, home to billions of people, face the imminent threat of inundation. Small island nations are particularly vulnerable, with entire communities at risk of displacement. The encroaching sea poses a direct threat to biodiversity, impacting marine ecosystems and exacerbating the loss of critical habitats for various species.
Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Disruption:
Climate change disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to widespread biodiversity loss. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and habitat destruction challenge the adaptability of many plant and animal species. This loss of biodiversity not only diminishes the beauty of our natural world but also weakens ecosystems’ resilience, making them more susceptible to diseases, invasive species, and further environmental degradation.
Agricultural Challenges and Food Security:
Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns pose significant challenges to agriculture, impacting crop yields and food production. Unpredictable weather events, such as floods, droughts, and heatwaves, can result in crop failures, threatening global food security.
Health Impacts and the Spread of Diseases:
The repercussions of climate change extend beyond the environment and into the realm of public health. Changing climate patterns contribute to the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease. Extreme heat events can also pose direct threats to human health, leading to heat-related illnesses and fatalities. Vulnerable populations, particularly in developing nations, face heightened risks, amplifying existing health disparities.
Economic Consequences and Social Inequities:
The economic toll of climate change is staggering, affecting industries ranging from agriculture and fisheries to insurance and tourism. The costs associated with adapting to and mitigating the impacts of climate change are substantial, and the burden is often disproportionately borne by marginalized communities. Social inequities are exacerbated as vulnerable populations face heightened exposure to climate-related risks without adequate resources for adaptation.
Conclusion:
The impact of climate change is a complex tapestry woven with environmental, social, and economic threads. Urgent and collective action is required to mitigate the current and future consequences of this crisis. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, invest in sustainable technologies, and foster resilience in vulnerable communities. Only through a concerted effort can we hope to address the challenges posed by climate change and build a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.